- Properties
- Synthesis
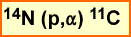
- T1/2 = 20 minutes
- It has a short T1/2 and requires the use of an in-house cyclotron
- Synthesis
- 11C-sodium acetate 👍
- Can be used to image the heart, prostate cancer, and Hepatocellular carcinoma
- In general, it measures oxidative metabolism
- Protein synthesis occurs and displays increased uptake as this level increases
- Is the smallest of all fatty acid
- Follows the acetyl-coenzyme pathway (COA)
- The body eliminates this agent by the release the of 11C20
- Prostate Imaging
- In theory acetate uptake will occur in metabolically active (rapid growth) tumor cells that live in a a low oxygen environment and have a high lipid pool
- Uptake may also relate to the testosterone, which may stimulate cancer growth
- The effectiveness of imaging prostate appears to be the primary reason to use the PET tracer. It may help define the extent of and determine treatment options for disease (ex. level of surgery vs. radiation)
- Interesting point - because elimination occurs by the exhalation of 11CO2 no urinary activity is noted. Such is not the case, if one where to evaluate the prostate bed with FDG
- Still in Clinical trails and current information
- Application in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)
- As with prostate imaging uptake is associated with increased lipids within the tumor site and the rate of cell growth
- Additionally, there is no hepatocellular excretion of carbon though the hepatobiliary tree, therefore enhancing target to background
- Appears to be more sensitive and specific for HCC7
- Cardiac Imaging
- Uptake is identified when blood flow reaches viable myocardial cells where acetate is extracted when the heart is in its oxidative state
- Reduced or lack of uptake is an indication that there is poor or no oxygen turnover in myocardial tissue
- Therefore, 11C-acetate evaluates oxygen utilization
- This tracer has been used to assess patients with stable chronic coronary disease or post myocardial infarction
- 18FDG and 11C-acetate can be combined to evaluate myocardial ischemia. In this process 11C-acetate has reduced uptake with ischemic cells because of the low level of oxygen. (oxidative metabolism requires a aerobic environment)
- 18FDG demonstrate increased glucose utilization (and uptake) because uptake occurs with anaerobic glycolysis, which indicate a highly ischemic area
- Lack of uptake with both agents defines an infarct
- There is an apparent relationship between acetate and 15O for myocardial perfusion imaging11
- Similar physiologic finding can be noted with 11C-pamitate
- Article compares the clinical use of this tracer with FDG8
- Imaging procedure
- After 4 to 6 hours NPO inject 20 mCi IV
- Dynamic imaging can be done over the area of interest
- Post five minutes injection a perfusion scan can be completed in a whole body/limited bed position format
- 11C-glucose
- There may be some application to brain and cardiac imaging
- Current literature shows limited application of this radiopharmaceutical with not that many articles written on this topic
- Twenty-one dogs were evaluated with FDG and 11C-glucse with the later being the superior agent9
- 11C-methylspiperone
- Used to assess neurological disorders
- Has a high affinity of D2 receptors that shows upregulation
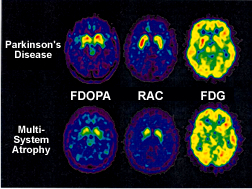
- Comparison of 11C-racolpride and 11C-methylspiperone shows upregulation with Parkinson's disease10
- 11C-methionine
- This amino acid is used to image glial tumors and pituitary adenomas
- Certain tumors, such as glial, have higher concentrations of amino acids
- Uptake is seen as a ratio where the concentration of the radionuclide within the tumor is compared to its concentration in health tissue
- In addition, the amount of tracer uptake is indicative of low vs. high-grade tumor
- 11C-choline (approved by CMS) 👍
- Has an affinity for certain cancers: prostate, colon, bladder, hepatocellular, and gynecologic
- This tracer incorporates into the tumor cell membranes that are composed of phospholipids and specifically phosphatidylcholine where choline becomes an component of the cell membrane
- Hence showing fatty acid metabolism via the cell membrane
- Does not excrete through the urinary system and therefore enhances target to background in the prostate bed and can be associated lymph node involvement
- Imaging procedure
- On a fasting patient
- Injected and acquire a 45 minute delay
- 18F-choline (👍) can also be used for this purpose and have similar results
- 11C-palmitate👍
- Similar to 11C-acetate with the main difference being its a larger fatty acid
- Literature mainly focused on the myocardium
- If the heart's in a fasting state its oxidative metabolism extracts fatty acid for energy
- In the presences of excessive glucose, palmitate uptake will be reduced and/or washout rate will increase
- Palmitate is a long chain fatty acid
- Approximately 70 - 90% is immediately utilized with <30% stored in the triglyceride pool
- There are two uptake phases (early and late) referred to as bi-exponential
- Early phase, 50% extraction fraction, relates to oxygen consumption in which beta-oxidation cause palmitate to form 11C-acyl-CoA and release of 11CO2 within tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle of the mitochondria
- Second phase incorporation triglyceride and phospholipids. The involvement of exogenous fatty acids may complicates the data. For this reason 11C-acetate is preferred since there seems to have little to no involvement of exogenous fatty acid uptake. Consider acetate as a shorter fatty acid chain and how this could enhance physiological uptake
- For myocardial assessment refer to 11C-acetate
- Apparently this radiotracer can also be used to assess the oxidative state of the brain where 50 - 60% of its oxidation will produce 11CO2
- The frustration of evaluating this radiotracer is simple -- there are too many animal studies and not enough human
- Image - 5 minutes post injection
- Properties

- T1/2 = 110 minutes
- 18F - NaF 👍 γ
- Is a salt
- Goes to calcium hydroxyapatite and exchanges with (PO4-) hydroxyl group
- Currently approved as a bone imaging agent for metastatic disease
- Unlike MDP, it displays lytic and blastic properties
- Image - 1 to 2 hours post injection
- 18FDG 👍 γ
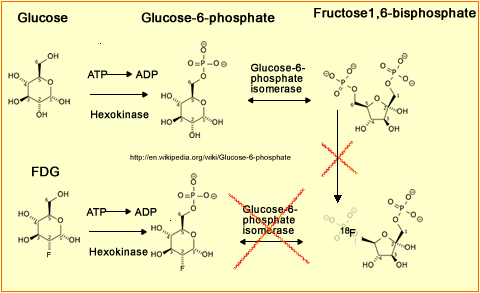
- FDG as a "fake" sugar
- As noted above, fluorine replaces one of the hydroxyl groups on the carbon ring
- Metabolically active tissue within the human body (normal tissue/disease) that requires glucose will pickup and initially metabolized FDG . Within the cell it phosphorylates by adding a phosphate to the ring via hexokinase. It becomes FDG (or) glucose-6-phosphate. However, since fluorine has taken over an OH this fake sugar can no longer be metabolized. Dephosphorylation occurs, glycolysis stops, and the FDG gets locked into the cell
- If radioactive glucose had been labeled (11C-glucose) it would eventually leave the cell, therefore, rendering it a useless imaging agent
- FDG is an excellent metabolically active tracer that goes to areas of disease and human system the require sugar
- Normal uptake is seen
- Brain - only uses glucose
- Nasopharyngeal
- Myocardium uses both fatty acid and glucose and therefore uptake depends on its metabolic state
- Muscle uptake uptake occurs when the tissue is active. For this reason, after a patient is injected it is required that he/she not move around until his/her imaging time. Consider issues such as reading a book while waiting (eye/hand movement) or tapping their foot as the listen to music. Furthermore a patient should not exercise for at least 24 hours prior to his/her PET exam
- Liver, spleen, reproductive are metabolically active
- Kidney/bladder is seen since FDG is excreted (normally glucose is not excreted by the kidneys)
- Inflammation does pickup FDG
- Consider the issue of infection and cancer residing with the body
- If uptake is seen and the technologist wishes to rule out infection, additional delayed imaging is required
- Comparing SUVs on these two data sets would reveal an infection is there was a decrease in the SUV value
- Consider tumor vs inflammatory uptake, tumor increases over time with the best target to background occurring at 90 minutes post injection
- Oncology
- At present the following cancers are being imaged with this radiopharmaceutical: breast, colorectal, esophageal, head and neck, lung (non-small cell), lymphoma, melanoma, single pulmonary nodule, and thyroid cancer
- Imaging cancer may be done for: initial diagnosis, staging, restaging, pre-chemo/radiation therapy, during/post chemo/radiation therapy, and pre-surgical planning
- Neurology
- Seizure evaluation prior to surgical intervention
- Mental disorders
- Tumor viability
- Cardiac
- Primarily done for myocardial viability
- Not done to analyze ischemia vs. infarct
- Imaging
- Oncology - inject and image 45 to 120 minutes post dose, where max uptake usually occurs at 45 minutes
- Brain - Setup IV prior to injecting and wait 15 minutes before injection. Delay imaging can occur between 30-60 minutes post dose
- Cardiac - Elevated sugar level, inject once the sugar level starts to drop. Then scan 30 minutes post dose
- 18F-Choline or Fluorocholine (FCH) 👍
- Pathology is similar to 11C-Choline
- Applied in many types of cancer which include: mostly prostrate, brain, and colon
- Procedure - In a fasting patient administer 5 - 7 mCi and start imaging in 15 to 20 minutes
- 18Fluoroethylcholine
- Biodistribution
- 18F-FECh enters tumor cells by active transport
- Via phosphorylation it becomes phosphory l-18F-FECh which in turn becomes a phospholipid
- This agent has a high avidity for prostate cancer and has similar biodistribution prosperities seen with 11C-Choline. There are two differences
- FECh excretes significantly faster then Choline
- Spatial resolution - better with the fluorine tracer which may relate to the distance traveled by the beta particle
- Biodistribution
- 18Fluorothymidine (FLT) markers of proliferation (5)👍
- Detects amino acid synthesis at the cellular level, which occurs in the DNA. FLT becomes trapped inside the cell via phosphorylation by thymidine kinase-1 (which is an enzyme). Thymidine kinase-1 is seen in high concentrations where there is significant cellular growth, ie. malignant cells. Uptake has been seen in colorectal/lung cancers
- Unlike FDG, It does not accumulate in inflammatory lesions
- Can be used for diagnosis of disease and evaluate the effectiveness of therapy
- Production of this tracer is very poor and will yield between 8 - 14% and needs a high-performance liquid chromatography added to the synthesis module
- Imaging
- Administer 7 to 10 mCi
- Data can be acquired dynamically or
- WB 1 hr post injection
- Biodistribution: bone uptake, hepatic uptake, no brain uptake, no GI uptake
- Images many types of cancer
- 18F-Fluoromisonidazole (FMISO) (6)👍
- FMISO is a derivative from nitroimidzole (type of antibiotic) and is trapped within cells that are hypoxic
- Understanding the physiology of tumor growth
- Often blood flow cannot keep up with excessive tumor growth, which results in a hypoxic state
- In addition, it is believed that tumor progression within the hypoxic state makes these cells more resistant to radiation/chemotherapy
- Another application is with myocardial viability
- FMISO is found exclusively in hypoxic areas at 1 - 5 minutes post injection.
- High levels have been found in high grade gliomas, but not in low grade
- Patient should be NPO before administering a 10 mCi dose
- Dynamic images can be taken to evaluate FMISO uptake in tumor and/or
- Whole body 2 hour delay
- May be used for monitoring and directing hypoxic therapy or
- Hypoxic myocardium
- 18F Flourodopa (F-Dopa) 👍
- Usually used to image Parkinson's disease (PD) and in neuroendocrine tumors
- In Parkinson's disease, the receptor sites do not function well and F-Dopa becomes flourodopamine via aromatic amino acid decarboxylkase (AAAD). Because there is degeneration on the pre-synaptic side PD cannot be converted to flourodopamine causing decreased uptake in the effected area
- Medications must be held for 12 hours prior to the injection
- Pretreat of 150 mg carbidopa to inhibit metabolites (60 to 90 prior to injection)
- Imaging - Usually done dynamic
- 18F Flurpiridaz (need to know)
- Cardiac imaging agent that is in phase three trials, as of 3/18
- Binds to mitochondrail complex 1 with an extraction fraction of greater than 90%
- Allows for absolute qualification of myocardial blood flow
- Flucicolvine (Axumin) 👍 γ
- Synthetic amino acid mimics glutamine transporter present in prostate cancer
- Approved for recurrence of prostate cancer
- <1.0 PSA levels tend to have low sensitivity
- 93% with >2.0 PSA level
- SNMMIT Review - 68Ga-PMSA-11 has been approved and appears to be better in detecting smaller lymph nodes. However, Axumin is superior when it comes to detecting recurrence of disease
- SNMMI information - https://www.snmmi.org/Patients/Procedures/Content.aspx?ItemNumber=30482
- 68Ga-PMSA-11
- 68Ga Gozetotide (Locametz)👍
- This is a transmembrane protein found in prostate tissue. Increase of prostate tissue (cancer) yields visual uptake
- Recommended for patients that have a Gleason sum of 7 or greater
- Dose between 0.049 and 0.06 mCi/kg
- Take one hour delayed whole body. However, greater lesion detection has been report with 3-4 hour delayed images
- Procedure standard
- Properties
- T1/2 - 10 minutes
- Primarily used to image the myocardium
- Has been shown to have some utilization in brain imaging
- Its T1/2 requires the use of an in-house cyclotron
- Article on the 3NH3 application -https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6382649/
- 13N-aminona as s Cardiac agent
- Primarily uptake occurs via blood flow to the myocardium, however, as flow rates increase uptake plateaus
- Uptake of 13NH3
- In the vascular pool this agent is mostly in its ionic form 13NH4
- When extracted by the cells it converts back to 13NH3 which makes it lipid soluble, crossing the cell membrane of myocytes
- Trapping occurs within the cells via glutaminic acid becoming 13N-glutamine
- This radio-agent is used as a myocardial perfusion agent, however, while looking around the Internet I discovered an unusual application for myocardial viability
- While 13NH3 is used as a myocardial perfusion usually in bariatric patients, below is an example of identifying hibernating myocardium that is very ischemic and has an anaerobic environment
- As long as there is some form of blood flow then13NH3 will be picked up by the viable tissue. It is synthesize to [13N]Glutamine
- It should be noted that glutamine, an amino acid, crosses the BBB is an essential component in states of illness and injury
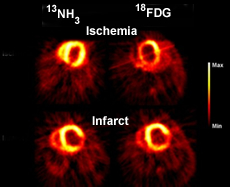
http://www.nmr.mgh.harvard.edu/martinos/research/technologiesPET.php - The above images compare13NH3 and FDG in the ability to identify ischemia/infarct. Based on the available data13NH3 seems to be the superior agent for cardiac viability. Question - Would13NH3 be considered an appropriate radiopharmaceutical for a cardiac stress/rest procedure? Yes.
- The oddity of the above images is that FDG should be the agent that is picked up by myocardium that has very poor blood flow, however, 13NH3 does a better job over FDG
- As a general rule FDG is still the agent of choice for heart issue that is in an hypoxic state. What we see above is an exception to the rule
- After patient has been NPO for 4 - 6 hours a 15 mCi dose is administered
- 2 - 3 minutes post injection resting images are taken
- Approximately 30 minutes later the patient is pharmacologically stressed and a second dose is administered
- Images are then acquired at 2 - 3 minutes post dose
- Properties

- T1/2 = 2 minutes
- Used to analyze brain and heart
- In-house cyclotron required
- H215O and/or C15O are used
- Biodistribution-water👍
- General
- Diffuses easily into tissue making it an excellent perfusion agent
- Used to assess cerebral and myocardial blood flow (MBF). Gold standard for assessing blood flow
- Repeated images can be done over a short period of time to evaluate different oxidative states (ex. different types of brain stimulation)
- Cardiac
- In general, this agent continues to increase in its extraction fraction as blood flow increase and reach ~100%
- Stress and rest images cannot be done in one imaging session because its T1/2 is to short
- 15O water can be administered, however, high levels of activity remain in the vascular pool
- If radio-labeled water is administered blood volume images must be corrected with C15O. For this reason other PET cardiac agents are recommended
- The main issue is that there is a lot of background
- Brain
- Used to analyze blood flow to the brain
- Oncology
- Assess perfusion in tumor(s)
- Biodistribution-gas 👍
- 14N gas is radiated to form 15O
- Evaluation of oxygen via its flow, volume, ad metabolic uptake
- Single bed position and shot in a dynamic mode
- Best used to evaluate regional blood flow to the brain
- n-15O-butanol
- Can be used to analyze blood flow to the brain as well as flow to other areas of the body
- Consider the partition coefficient of 15O - water is 0.9 where 15O-butanol is 1.0
- What does partition mean? Relates to compound solubility. Butanol has better solubility and may be "slightly" better agent to evaluate MBF
- Properties
- Parent - 82Sr has a 25.6 day T1 /2
- Daughter - 82RbCl has a 76 second T1/2
- 0.02 μCi/mCi is the breakthrough limit of Sr. This is checked daily, prior to patient use
- Is administered through an infusion system
- 40 - 60 mCi. Generator recharges in 10 minutes
- Extraction fraction of myocardial tissue is 50 - 60% (however, difficult to assess correctly)
- Procedure
- Biodistribution
- Evaluates blood flow to the myocardium
- Is an analog to potassium and is picked up by myocardial tissue via active transport
- Uptake increases with increased blood flow increases, however, at high flow rates the extraction levels off (just like thallium)
- For the above reason, quantification is not recommended
- It has poor blood clearance in the blood pool and has a limited T1 /2 . Therefore, activity is present within the cardiac chambers even as it perfuses into cardiac tissue. This requires a subtraction technique when images are processed
- According to Stankewicz, MA, et. al. 82Rb is not a good predictor for myocardial viability
- Calibrated with 42 mCi @ 8:00 for the specific clinical day that it is needed
- T1/2parent is 38 hrs T1/2 daughter is 12.7 hours
- Perfusion agents and lipophilic, with uptake normally seen in kidneys, heart, liver, lungs, and others
- Agent is then tagged to several different compounds
- 64Cu-ETS (Green MA, et al)
- Appears to be best suited for renal imaging defining renal perfusion
- There may also be applications with hypoxia and/or perfusion(Zhang T, et al)
- 64Cu-PTSM
- Used to evaluate lung mass by visualizing hypoxia and perfusion with ETS and PTSM (Zhang T, et al)
- Can assess rCBF
- Vascularity/blood flow in tumor
- Appears to be used assessing ischemic disease of the heart
- 64Cu-ATSM
- Appears to be best suited for renal imaging defining regional perfusion and may be able to define actual blood concentrations of ETS
- Zhang makes similar comments to PTSM
- Similar structure to the above two agents and is also lipophilic, however, it generally washes out quickly in normal tissue, but retained in tissue that is hypoxic
- 64Cu-dotatate 👍
- SSTR2 site on neuroendocrine tumors
- The only advantage appears to be that copper has a longer T1/2 when compared to gallium
- Related article - https://jnm.snmjournals.org/content/62/1/73
- 64Cu-ETS (Green MA, et al)
- 68Ge/68Ga is a generator that has a parent T1 /2 of 271 days and a daughter of 68 minutes
- Via a cyclotron 68Ge is made: 68Zn(p,n)68Ge
- The elution used is 0.1NHCl
- Tagging 68Ga to DOTATATE takes about an hour
- General statement - all DOTAs' bind to SST 2 receptors in neuroendocrine tumors, however, some have greater affinity for other receptor sites
- The daughter can be tagged to several types of agents that goes to somatostatin tumors, hence this is a neuroendocrine tracer
- Literature review - these generators hare radiolabeled somatostatin analogs that have an affinity for somatostatin receptors (SST) found on neuroendocrine tumors
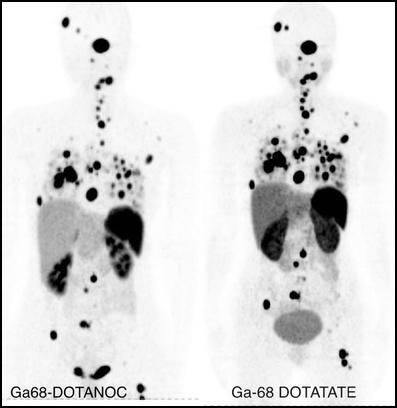
- Yang et al 68Ga-DOTANOC and 68Ga-DOTATATE are both accurate in diagnosing disease
- Peoppel, et al 68Ga-DOTANOC and 68Ga-DOTANOC give similar results, however, is limited with DOTATATE having a greater affinity (x10) of the somatostatin receptors subset 2 (sst2). These SST receptors are found on neuroendocrine tumors
- Kabasakal, L, et al Compared 68G DOTATATE to 68Ga DOTANOC and showed that both agents were effective in defining neuroendocrine tumors, however, with 68G DOTATATE having greater uptake within the tumor
http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00259-012-2123-y - Procedure
- Inject 3 to 5 mCi
- Dynamic images may be taken
- Delayed images start at 60 - 90 minutes post dose
- Whole body images are taken
- Production 124Te(p,n)124I or 124 Te(d,2n)124I - More information of the process
- Literature review
- Phan HT, et al Increased sensitivity identified when patients with thyroid cancer (DTC) had 124I PET imaging. Furthermore uptake was not always seen with 131I. Whole body procedures revealed increased uptake and improved resolution with 124I when compared to 131I. While there were concomitant results with both iodines, 131I missed more disease when compared to 124I. The population size under investigate was 20
- Ruhlmann, M, et al A larger study containing 127 were evaluated with 131I and 124I - PET agent can be used for staging and treatment planning
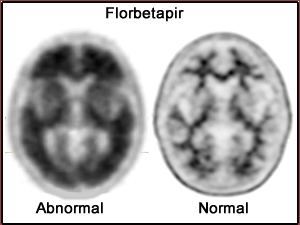
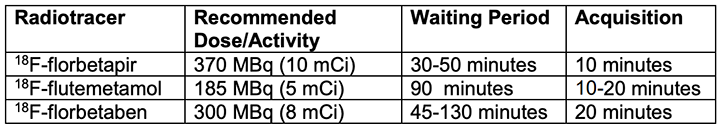
- 18F -florbetapir (Amyvid from Eli Lilly) image 30 to 50 min post dose for 10 minutes - summery
- 18F -flutemetamol (Vizamyl from GE Healthcare) - recommended dose 5 mCi
- 18F -florbetaben (NeuraCeq from Piramal Pharma) - dose not to exceed 10 mCi
- Used to access the amount of β-amyloid protein that is usually found in the gray matter with patients that have Alzheimer's disease
- 18F - Flortaucipir (Tauvid) targets tau protein instead of β-amyloid. Dose is ~10 mCi
- Typical FDG brain preps are not required
- No quiet room with low lighting
- No waiting after setting IV
- No glucose check
- Abnormal uptake identifies a significant concentration of β-amyloid protein
- . F-18 Fluoroestradiol (Cerianna) FES 👍
- Synthetic derivative of estradiol and is classified as a estrogen hormone
- Binds to estrogen receptors, mostly alpha (ERα) and will bind to tumors that have this receptor site
- endometrial, ovarian, and certain prostate cancer may also have ERα receptors
- Dose 3 - 6 mCi. Imaging usually occurs between 20 and 80 minutes post dose