- General comments about Technetium agents
that cross the BBB
- Brain agents that are lipophilic cross the BBB
- Uptake by the neurons occurs via passive diffusion
- It is best compared with an rCBF (rate of Cerebral Blood Flow)
- These technetium brain agents where initial tested and compared with 133Xe
- Above is an example of a rCBF system shows 64 detectors that evaluate Xenon distribution within the brain
- Each tube has a PMT with NaI crystal attached to its proximal end
- HMPAO was the first agent approved for brain perfusion. Later ECD became available
- These radiopharmaceuticals cross the BBB and can identify a host of disease, however, they were initially developed to diagnose CVA
- Regarding CVA - ECD and HMPAO are more sensitive than CT and MRI because these radiotracers show immediate loss of blood flow to the affected site, while CT may take as much as 12 hours
- Following thrombolytic therapy (to break up the clot) these radiotracer can identify re-vascularization
- Scenario - (Workup to the use of ECD or HMPAO) Once a suspected CVA has occurred there is an approximate 2 - 3 hour window (according to radiology) were thrombolytic therapy can be given (TPA - tissue plasminogen activators). Let us assume you have a patient has arrives in the ER at 1am with a suspected stroke (personal experience)
- The First aspect to consider - how long ago did the symptoms start? Five minutes ago or longer. Point is, the clock starts ticking on the first sign of any symptom
- The problem is identified (tick tick) and order is written and the nuclear medicine technologist is called in
- Technologist calls the central pharmacy
(tick tick)
- Pharmacists drive to work
- Milks generator and compound's the radiopharmaceutical and then completes QC
(how much time has gone by since the first symptom?)
- Dose than travels to your hospital
- Dose arrives, logged in, measured, and administered IV
- Fifteen minutes post IV the SPECT procedure can be started
- Scanning time about 1/2 hour
- Processing time 10 - 15 minutes
- Doctor reviewing of the results
and the procedure is found positive for CVA
- Administer TPA.
- Did all this happen within the 2 - 3 hours window?
- 99mTc-hexamethyl propylene amine oxime (HMPAO)
- At first pass, 72% is as it crosses the BBB
- This initially lipophilic compound becomes hydrophilic after it attaches to a neuron
- Extraction - 59 mL/minute per 100 grams
- Part of the agent will diffuse back into the bloodstream
- It reaches equilibrium within 2 minutes and stays constant for 8 hours
- Methylene blue creates a stabilizes product for four hours
- Without methylene blue
- Stable for only 1/2 hour
- Generator elution must be less than 2 hours old
- It does not redistribute
- Has a slower washout rate when compared to ECD
- 99mTc -ethyl cysteinate dimmer (ECD)
- Similar to HMPAO
- Lipophilic becomes lipophobic when it attaches to a neuron
- Extraction - 50 mL/minute per 100 grams
- Approximately 6.5% of the dose is retained by the brain in 5 minutes. 5.2% in 1 hour and 3.8% in 4 hours
- The expiration time is six hours
- Issue - Final stage of compounding requires it to incubate for 30 minutes
- As for an advantage over HMPAO - imaging can be done sooner and target to background is better
- Here is a comparison of HMPAO to ECD - One must note that the purpose of these images was to as ictal and interictal states
- Is there an advantage of one agent over the other?
- 133Xe
- The original rCBF (rate of cerebral blood flow) agent
- Imaging
- Initially analyzed the brain via a helmet placed over the patients head and then 133Xe is inhaled
- PM tubes are placed around the helmet to map blood flow

http://www.ceretronix.dk/cortexpl.htm
- The above map shows xenon distribution with normal brain function vs. a patient with Alzheimer's
- Data is collected on wash-in and washout rates from the inhalation of this radioactive gas
- The above technetium agents were compared with 133Xe to determine the effectiveness of the 99mTc agents
- This procedure is still done in a limited amount of imaging centers
- SPECT procedure
- A three-headed camera is the most ideal method of imaging
- LEHR collimator
- 64 or 128 matrix images are acquired for at least 20 seconds
- 64 or 128 stops
- 360-degree rotation
- Images are then processed and displayed
- Below is an example of a normal brain with the anatomy labeled
- Another perspective in evaluating the anatomy is to consider the different lobes of the brain, as noted below
- Diagnosing brain diseases and disorders via NMT
- CVA
- Types
- Occlusive or thrombotic strokes that occlude large arteries
- Embolic strokes is like "PE"
- Hemorrhagic strokes occurs when blood leaks into the brain tissue
- These agents will detect a CVA immediately (it all about blood flow)
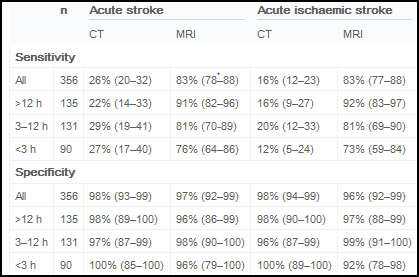
- CT may be better utilized with patient that have a hemorrhagic stroke
- MRI is not always immediately positive
- Sensitivity and specificity MRI compared to CT is noted above. Overall it seems that MRI is the diagnostic tool of choice.1
- Loss of blood flow results in a perfusion defect when using ECD or HMPAO
- ECD and HMPAO may still be more sensitive in finding disease
- In one article, ECD was shown to better define a patient's prognosis. Where MRI showed defects of acute stroke, ECD was able to show better delayed outcomes that included prognosis and rehab counceling.2
- Recent literature on ECD and HMPAO seem limited - 7/23/2012
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA)
- Most imaging appears normal when CT is used
- As high as 60% of SPECT imaging will show lack of blood flow
- TIA leads to CVA
- If defect is seen in SPECT scan showing TIA, there is a correlation to having a CVA in the future
- Pharmaceutical intervention to analyze brain function
- Acetazolamide (AZT) has vasodilation properties
- Looking for ischemic arterial circulation
- which may be clinically seen as a TIA
- This is a two part test
- Administer AZT 1gm IV for over 2 minutes
- Monitor patient for 25 minutes to include BP
- Inject 20 - 30 mCi of HMPAO or ECD
- Wait ~ 20 minutes and complete a SPECT scan
- Repeat procedure 24 to 48 hours later without pharmacological intervention
- Remember your heart + vasodilator = coronary steal? The same concept occurs with the brain and its blood flow with the end result being, lack of uptake. Let's call this "neuronal steal"
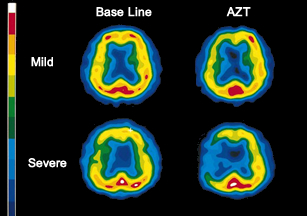
- Kim JS, et al. evaluated 75 patients with possible contra-lateral carotid stenosis (>70%) and prior to surgical intervention.
- Poor cerebrovascular reserve indication that there is reduced blood flood making the patient a candidate for carotid endarterectomy
- AZT with 99mTc-ECD SPECT seems to complement the diagnosis of carotid stenosis as noted in the above images
- Dementia
- Alzheimer's disease (AD) occurs in 3/4 of all dementia patients where hypo-perfusion is seen in the effected tissue
- Parietal deficit more sensitive to disease
- Posterior cingulate
- Frontal cortex (usually late)
- Reduced metabolism in brain tissue via neuronal depletion results in perfusion defects
- Classic patterns of abnormal uptake are usually seen in the temporoparietal regions (maybe more on one side than the other, but bilateral defects are possible) with more severe AD showing frontal lobe abnormalities
- Other forms of dementia may have similar patterns seen on AD
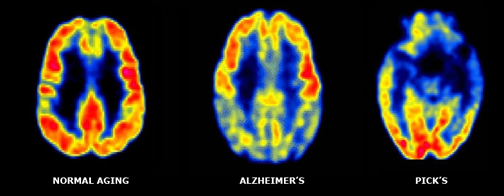
- Picks disease is a form of dementia that involves the frontotemporal areas of the brain. Notice the difference between a Normal - Alzheimer's - Pick's
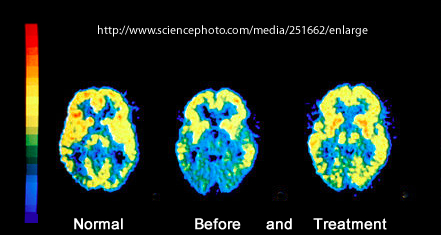
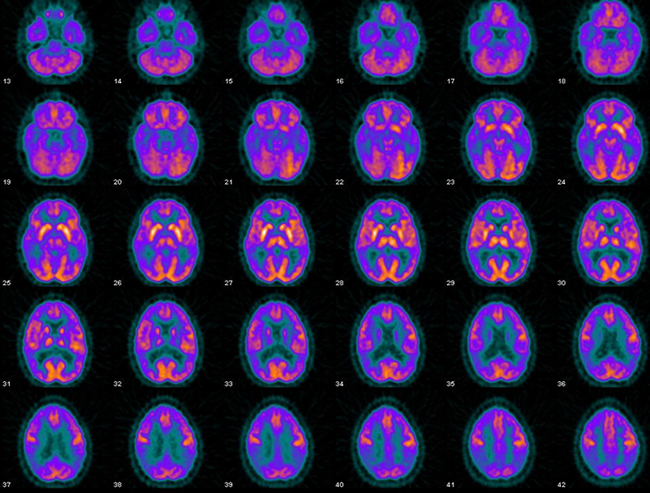
- AIDS dementia usually show defects in the frontal and temporoparietal cortex
- Normal vs. AIDS dementia shows loss of uptake and atrophy with FDG PET
- Treatment of anit-retroviral drug for 13 weeks shows improved uptake with increase in glucose metabolism
- Substance abuse (ex. History of crack/cocaine and heroin show similar defects seen in AIDS dementia)

- Here is an example of too much Kola. Cocaine reduces blood flow which can lead to minor infarcts
- Seizure - Epilepsy
- Two types
- Grand mall
- Partial or temporal lobe epilepsy, simple and complex
- NMT's goal is to Identifying the site of the seizure
- EEC studies can not define the area in the brain that causes the seizure
- Using HMPAO or ECD can be done when the patient is in an interictal state (no seizure)
- During the ictal state (when the patient is having the seizure) the radiopharmaceutical is re-injected and the patient is scanned a second time
- Results may indicated
- During the interictal state, the area causing the seizure may show reduced blood flow
- During the ictal state the area of the seizure will have increased blood flow indicating a hot focal site of activity
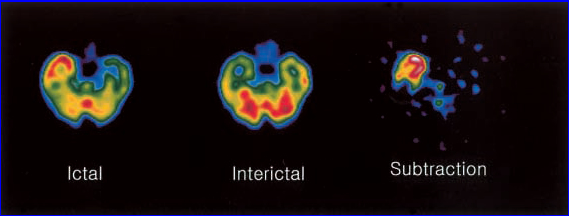
- Surgery may then be applied to destroy the site causing the seizure
- 123 I-IMP is the best radiopharmaceutical to determine the ictal site (based on half-life), however, it is not currently available in the US market
- Head injuries
- Following an MVA a perfusion SPECT brain scan may be ordered
- Viable brain tissue will pick up the radiopharmaceutical while damaged tissue will show lack of activity
- This may help in determining the patients' prognosis and may be more useful than CT or MRI
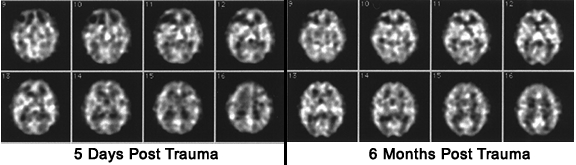
- Stamatakis EA, et al evaluated 61 patients with head injuries and compared MRI to 99mTc-HMPAO
- The article specifically evaluated statistical parametric mapping (SPM) with SPECT to detect hypoperfusion. It was determined that SPECT identified more focal and diffused injury
- The purpose of the above images is to show you how SPECT brain imaging can be used to assess improvement (or the lack of) in blood flow to traumatic brain injury
- Psychiatric disorders
- Major depression disorders and bipolar disease usually show reduction in cortical blood flow
- Schizophrenia usually appears as low uptake to the frontal lobe
- May also show increased striatal flow
- Patients that are being medicated for this disease may have his/her defect resolve
- Brain tumors
- Usually imaged with CT and/or MRI
- However, when radiation therapy has been administered, necrosis and inflammation may hide residual tumor
- 201Tl and 99mTc-sestamibi have shown a high affinity for detecting viable tumor. Drawing ROIs around normal tissue and tumor may give the following results
- 3.5 to 1.94 - tumor to non-tumor is an indication of a high-grade lesion
- 1.95 to 1.0 - tumor to non-tumor is an indication of a low-grade tumor
- ROI data was determined with 201Tl
- Brain Death
- Agents that don't cross the BBB show lack of blood flow to the brain during the dynamic procedure.
- If the radiotracer crosses the BBB then a flow study is not needed, it just becomes a matter of uptake
- Lack of activity in the skull indicates brain death. Sometime referred to as the "hollow head"
- You we use a tracer that crosses the BBB or one that does not? Let's talk about it! Consider
- ECD and HMPAO are slightly better and much more expensive
- DTPA and GH are very inexpensive
- SNM procedure Guideline for Brain Death Scintigraphy
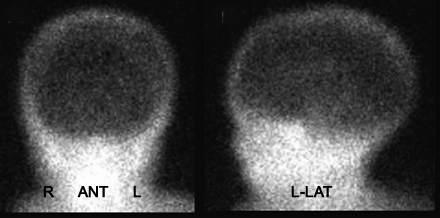
- Brain seen on a child. 99mTc-ECD was administered
- Brain receptor imaging
- There have been receptor ligands that have been developed with SPECT imaging agents
- Usually 123I is the radiotracer
- D1 and D2 dopamine receptors have been tested
- Uptake of the radiopharmaceutical indicates the utilization of the ligand to specific areas in the brain
- More on this when we discuss FDG Brain
- Comment on PET
- 18FDG can be used for brain imaging and maybe the study of choice when compared to perfusion SPECT (rCBF) agents
- PET radiopharmaceuticals other than FDG may also be used
- Link to PET Brain lecture
- A look at normal Brain vs. disease within the brain - presented by Harvard Medical
- The normal brain - PET-FDG and MRI
- Glioma FDG / Glioma 99mTc and 201Tl
- Alzheimer's
- Mild - FDG and MRI
- Moderate - FDG and fMRI
- AIDS dementia - 99mTc
- Other brain diseases
- We will talk more about this next semester, but here is an article on imaging amyloid plaque
1 - Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography in emergency assessment of patients with suspected acute stroke: a prospective comparison by Chaleta HA, et al
2 - Perfusion differences on SPECT and PWI in patients with acute ischemic stroke, Nuutinen J, et al. http://www.springerlink.com/content/g226h262wn31t116/fulltext.pdf