|
What is the difference between standard deviation and standard error? Some
typical answers ·
Formula…SE = SD/Ön ·
Standard deviation is
an average of the spread (or variability) of each data point from the overall
mean. Standard error is the average
variability of the sample means from the overall mean. ·
SE: This is related
to the estimates of parameters and it represents how much [deviation] from
the expected value of the estimate of the parameter. ·
Standard error is the
error of the particular test being used. [in the sense that it is related to the test statistic…] · The standard deviation is a measurement which contains a certain % of the data. For example, ± one st. dev. of the mean contains 68% of the data for a normal distribution. The standard error is something I cannot define. [an honest answer!!] |
|
What is a p-value? How does this differ from the significance level? Are these related to power? Some
typical answers ·
P-value is
probability of obtaining a value as extreme as the hypothesized/critical value. [say
“observed test statistic” instead] ·
P-value is the
probability of observing a response at or further from the overall
standardized mean response. ·
The p-value is
compared to the significance level to determine statistical significance. ·
The p-value is the
probability that a Type I error will occur. [not
correct] ·
P-value is the
probability to |
Notes:
The power function is the probability that the data provides sufficient evidence to support the research hypothesis (or reject the null hypothesis). How is the power function related to the p-value?
The p-value is a statistic and thus is subject to random variation (varies from sample to sample). When the observed p-value is less than or equal to the significance level – a – then the research hypothesis is supported. Let S denote the p-value. Then the probability of supporting the research hypothesis, the power function, is equal to the probability that S is less than or equal to the significance level.
Data: X1, X2, …, Xn are iid N(m, s2) where s2 is known but m is not.
Hypotheses: H0: m =m0 versus H1: m >m0
Test statistic: ![]() , which has a N(0,1)
distribution under H0 and a N(
, which has a N(0,1)
distribution under H0 and a N(![]() ,1) distribution in general.
,1) distribution in general.
Power function: ![]() , where
, where ![]() , the inverse of the standard normal cdf
at 1-a.
, the inverse of the standard normal cdf
at 1-a.
Thus 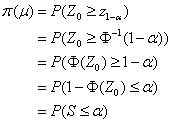 since
since
![]() .
.
When H0 is true, then![]() . Thus, in this
case, S has a standard uniform distribution.
. Thus, in this
case, S has a standard uniform distribution.