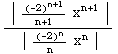_________________________________________________________________________________
Differential Equations Quiz
#8 April
29, 2005
Name____________________ R. Hammack Score
______
_________________________________________________________________________________
(1) Find the
general solution of the differential equation x y''+y'=x
First, let's find 
x y''+y'=0
 y''+x
y'=0
y''+x
y'=0
A.E.:  =0
=0
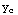 =
=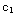 +
+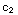 ln(x)
ln(x)
Next, apply variation of parameters to find 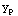 .
.
Standard Form: y''+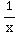 y'
= 1
y'
= 1
|
W=Det(
|
|
) =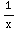 |
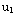 =∫
=∫ 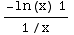 dx=-∫x
ln(x)dx = -
dx=-∫x
ln(x)dx = -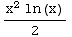 +
+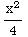 (by parts)
(by parts)
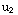 =∫
=∫ 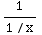 dx=∫x
dx =
dx=∫x
dx =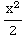
Thus 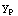 =-
=-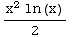 +
+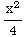 +
+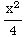 ln(x)
=
ln(x)
= 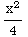
SOLUTION: y=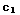 +
+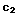 ln(x)
+
ln(x)
+ 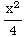
(2) Find the interval of
convergence of the power series ![Underoverscript[∑ , n = 2, arg3]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_25.gif)
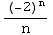
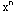
Ratio Test for Absolute Convergence:
![Underscript[lim , n∞]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_28.gif)
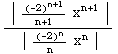 =
= ![Underscript[lim , n∞]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_30.gif)
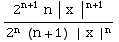 =
= ![Underscript[lim , n∞]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_32.gif) 2
2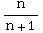 |x|
= 2|x|
|x|
= 2|x|
Thus, we get convergence if 2|x| <
1, or rather if -1/2 < x < 1/2.
What about the endpoint x = 1/2 ? Then the series becomes ![Underoverscript[∑ , n = 2, arg3]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_34.gif)
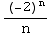
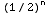 =
=![Underoverscript[∑ , n = 2, arg3]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_37.gif)
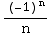 which
is the (convergent) alternating harmonic series.
which
is the (convergent) alternating harmonic series.
What about the endpoint x = -1/2 ? Then the series becomes ![Underoverscript[∑ , n = 2, arg3]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_39.gif)
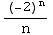
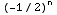 =
=![Underoverscript[∑ , n = 2, arg3]](HTMLFiles/Q8S05C_42.gif)
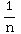 which
is the (divergent) harmonic series.
which
is the (divergent) harmonic series.
CONCLUSION: Interval of convergence
is (-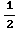 ,
,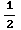 ]
]