NeutroSpec - Fanolesomab |
 |
The initial intent of this MoAb was to diagnose Appendicitis (a specific infectious process). Further evaluation may lead to diagnosing other inflammatory/infectious processes that will be discuss later in this lecture
- Currently the product has been taken of the market because of 2 deaths associated with its administration. For more information click here
- Package insert information
- Fanolesomab is an IgM Antibody, specifically anti-SSEA-1 with a molecular weight of ~900 kDa.
- It has high specificity for human neutrophils
- It has a high affinity for the carbohydrate moiety 3-fucosyl-N-acetyl lactosamine contained in the CD15 antigen, which is expressed on human neutrophils
- This allows the MoAb to tag to certain WBCs, specifically neutrophils, when injected into the vascular pool. After linking to the neutrophils the WBCs then travel to the site of infection
- Clinical trails
- Multicenter in nature
- Two-hundred patients with ages ranging from 5 to 86 that had equivocal signs of appendicitis were part of this study
- Some of the symptoms included: LRQ pain, pain increasing over time aggravated by movement or cough, LRQ tenderness, fever of plus 101o F, elevated white count, etc.
- Planar images (not SPECT) were taken and read blindly by readers and clinical investigators with the following results for diagnosing appendicitis
- Readers: 75% sensitivity, 93% specificity, and 87% accuracy
- Clinical Investigators: 91% sensitivity, 86% specificity, and 87% accuracy
- Of the patients that were positive
- 50% was positive within 4 minutes
- 100% was positive within the hour
- In an article/research ( Palestro, Caprioli, et. al.) on pedal osteomyelitis the diagnosis was attempted with 3-phase bone scan, 111In-WBC, and 99mTc-antigranulocyte (Fanolesomab). The following results are noted:
|
MoAb |
WBC |
3-Phase |
MoAb/Bone |
WBC/Bone |
Sensitivity |
90% |
80% |
90% |
90% |
80% |
Specificity |
67% |
67% |
27% |
67% |
75% |
Accuracy |
76% |
72% |
52% |
76% |
90% |
- Fanolesomab is currently approved for use of diagnosing appendicitis (nothing else - which effects reimbursement if the agent is being used to diagnose osteomyelitis)
- When compared to labeled WBCs the results are "similar" as seen in the above table
- Possible limitations regarding the research reported in this article
- This study evaluated a small population - 25 patients
- 111In was used instead of 99mTc for the labeling of WBCs. Literature indicates that 99mTc is slightly better in diagnosing osteomyelitis
- Biodistribution of Fanolesomab
- The first two T1/2 are 0.3 hrs and 8 hrs
- Site of infection
- Liver/spleen
- Kidneys
- Vascular pool
- Urinary bladder
- Video discussion of Fanolesomab pathophysiology
- HAMA concerns
- Anaphylaxis reaction is a concern and is mentioned in the package insert. To date 2 patients have died (cardiopulmonary failure) and 15 other have had a reaction
- What has been reported during the clinical trails?
- Of 439 patients only 30 reported any type of adverse event
- Most frequent - vasodilatation as flushing
- Dyspnea, paresthesia, headache, syncope, dizziness, and pharyngitis have also been reported in very low numbers
- Radiopharmaceutical compounding
- Must be refrigerated between 2 - 8o C
- Remove from refrigerator and let it warm to room temperature
- Aseptically add 20-40 mCi in a 0.2 to 0.35 mL volume of 99mTcO4- into the reaction vial
- Comments on 99mTcO4-
- Must have been eluted within the last 8 hours
- The generator's previous elution should be less than 24 hours
- Swirl and incubated at 37oC for 30 minutes
- Add 1 mL of Cenolate (ascorbic acid) in a 500 mg/mL concentration
- Assay and inject 10 - 20 mCi IV
- Procedure (several options)
- General comments regarding each option
- Collimation - LEHR
- 256 x 256 matrix
- 10 -15% window
- Option 1
- Dynamic mode
- Every 4 minutes for a total 40 minutes
- Option 2
- Static
- 1000k on the first image at 5 minutes post injection
- Preset all other images to time based on the first image
- Image every 5 to 10 minutes for 1 hour
- If Whole body
- At 1 hour post injection
- 256 x 1024 matrix
- 10cm/min
- If SPECT two headed
- 64 x 64 matrix or 128 x 128
- 30 sec/stop or 20 sec/stop
- Butterworth, cutoff: 0.5 or OSEM Subset 2, Iterations: 4
- Image at one hour post injection
Results
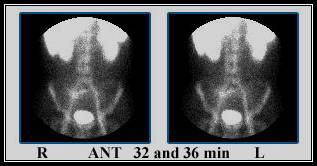
Case 1 - Demonstrates a normal scan with no abnormal accumulation of the radiotracer. Normal uptake is noted in the vascular pool, liver, spleen, kidney and urinary bladder
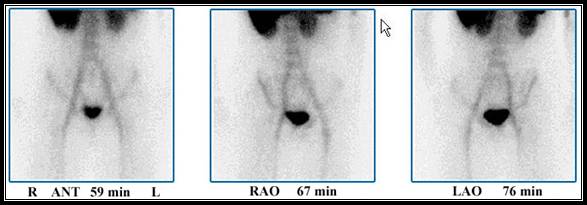
Case 2 - Abnormal uptake is noted in the LRQ of the patient where excessive activity is seen. This patient was taken immediately to surgery. An infected appendix was remove

Case 3 - Found at medGadget, "FDA Sounds Alarm on NeutroSpec."
Return to the Beginning of the Document
Return to the Table of Content
10/14




