Back
To Main
CULTURAL AND SOCIAL CONTEXT
OVERVIEW
The countercultural movement produced a very large potential recruit pool for new religious groups toward the end of the 1960s.
The initial membership base of a number of the movements of that era was young adults.
There were five major, overlapping streams of the 1960s-1970s countercultural movement.
● The anti-war movement
● The student protest movement
● The civil rights movement
● The drug subculture
● The feminist movement
VIETNAM WAR
1945-1954
● France was involved in a losing military struggle to maintain control over its colony. North Vietnam was established in 1954.
1955-1975
● The Vietnam War ensued between North and South with supporting allies.
1965
● The first American troops entered the conflict and the first protest movements formed.
1967
● The number of U.S. troops in Vietnam approached 500,000. Deaths reached 15,000 with 60% in 1967.
1968
● The massacre of 200-500 Vietnamese civilians at My Lai occurred.
● A major anti-war demonstration took place at the Democratic Convention in Chicago.
1969
● 500,000 marched in the largest antiwar rally in U.S. history.
● President Nixon announced 25,000 troop withdrawals.
● The death and injury toll of U.S. troops in Vietnam reached 100,000
1973
● Cease fire agreement signed and the last American troops withdrew.
STUDENT PROTEST MOVEMENTS
1964
● The Free Speech Movement was founded at U.C., Berkley and quickly combined student rights and anti-war activities.
1965
● Students for a Democratic Society organized “teach-ins” and anti-war marches.
1967
● 400,000 war protesters march from Central Park to the UN.
● Several celebrative festival style events (Flower Power Day in NYC, Monterey Pop Festival,
Summer Solstice Party in Golden Gate Park)
● The Graduate was filmed
1968
● Love-in at Malibu Canyon, California.
● Student demonstrations on college campuses (Columbia University, Boston University)
1969
● "Summer of Love" in San Francisco, Woodstock Festival draws 500,000.
● Hippies in People's Park in Berkeley attacked by police and National Guard.
● 300 colleges and universities experienced demonstrations, strikes, takeovers, class boycotts (U.C. Berkeley, U. Mass, Howard U., Penn State, U. of Wisconsin, Harvard U., City College NYC)
1970
● Over thirty percent of campuses experienced demonstrations.
● Four college students killed by National Guard at Kent State University, police kill two students at Jackson State University.
AMERICAN POPULATION GROWTH AND THE BABY BOOM
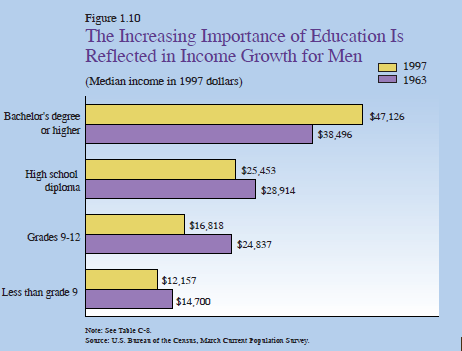
THE IMPORTANCE OF EDUCATION FOR INCOME
CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT
1960
● Sit-ins began and spread to 15 cities in 5 southern states.
● The Civil Rights Act of 1960 became law (penalties for obstructing right to vote)
1963
● Alabama Governor Wallace gives "Segregation Forever" speech at his inauguration.
● Martin Luther King Jr. gives his I Have a Dream speech.
● Four Black girls are murdered attending Sunday school in the bombing of the Sixteenth Street Baptist Church in Birmingham.
1964
● The Civil Rights Act of 1964 became law (making segregation in public facilities and discrimination in employment illegal).
● There were race riots in Philadelphia and Harlem, NY.
● Three civil rights volunteers working to register voters are murdered by southern whites.
1965
● The Voting Rights Act of 1965 became law, eliminating literacy tests and other restrictions on voting.
● Martin Luther King Jr. and other protesters were arrested in Selma and Montgomery, Alabama in protest activity.
● A major insurrection in Watts section of Los Angeles Major left 35 dead.
1967
● Rioting occurred throughout the summer in Chicago, Brooklyn, Cleveland and Baltimore, Newark, Detroit.
1968
● The Civil Rights Act of 1968 became law (prohibiting discrimination in the sale, rental, and financing of housing).
● The week following Martin Luther King Jr.'s murder there were black uprisings in 125 cities across the U.S.
1969
● The Supreme Court ordered desegregation nationwide
1971
● School busing to end segregation was upheld by Supreme Court.
● Shirley Chisholm became the first black woman to run for President
DRUG SUBCULTURE
1931
● By 1931, 29 states have outlawed marijuana.
1936
● The film “Reefer Madness” was released.
1937
● Congress passed the Marijuana Tax Act, effectively criminalizing marijuana by requiring individuals pay an excise tax for authorized medical and industrial use.
1944
● The New York Academy of Medicine issued a report finding that use of marijuana did not induce violence, insanity or sex crimes, or lead to addiction or other drug use.
1951-1956
● Federal drug laws were amended to read that a first-offense marijuana possession carried a minimum sentence of 2-10 years with a fine of up to $20,000.
1960
● Timothy Leary and Richard Alpert began experimenting with psychedelic drugs at Harvard.
1960s
● Reports commissioned by Presidents Kennedy and Johnson found that marijuana use did not induce violence nor lead to use of heavier drugs.
1966
● Timothy Leary was sentenced in Texas to 30 years for trying to cross into Mexico with a small amount of marijuana and later that year by G. Gordon Liddy for possession of marijuana.
● LSD was added to the list of illegal drugs.
● Timothy Leary announced the formation of a psychedelic religion (League for Spiritual Discovery) ("Turn on, tune in, drop out") and started nightly presentations at the Village Theater.
1966-1967
● Experimentation with marijuana and LSD doubled in one year
1968
● The FBI reported a 98% increase in marijuana arrests from 1966-1968.
1970
● Timothy Leary was sentenced to 10 years on marijuana charges but escaped from prison.
● Congress passed the Comprehensive Drug Abuse Prevention and Control Act, which categorized marijuana separately from other narcotics and eliminated mandatory federal sentences for possession of small amounts.
1971
● President Nixon named drug abuse as "public enemy number one in the United States."
1972
● The National Commission on Marijuana & Drug Abuse recommended legalization of marijuana. During the remainder of the decade 11 states decriminalized marijuana.
1973
● The Drug Enforcement Administration (DEA) is established.
● New York enacted the Rockefeller Drug Laws requiring lengthy prison terms for the possession or sale of a relatively small amount of drugs.
1975
● The Domestic Council Drug Abuse Task Force called for directing federal control efforts toward high risk drugs and names marijuana a "low priority drug."
FEMINIST MOVEMENT
1920
● The Nineteenth Amendment granted women the right to vote.
1960
● The FDA approved the first birth control pill for sale.
1961
● Betty Friedan's The Feminine Mystique was published.
1963
● The Presidential Commission on the Status of Women report found discrimination against women in every aspect of American life and outlined plans to achieve equality, emphasizing fair hiring, paid maternity leave and affordable childcare.
● The Equal Pay Act was passed requiring equal pay for men and women doing equal work.
1964
● The Civil Rights Act of 1964 barred employment discrimination on the basis of sex as well as race.
1965
● Griswold v. Connecticut struck down the only remaining state law (Connecticut) banning the use of contraceptives by married couples.
● The Weeks v. Southern Belle decision removed many restrictions on laws and practices on women's work and opens many previously all-male jobs to women.
1966
● The National Organization for Women was founded as a civil rights group.
1967
● The Equal Rights Amendment was introduced in the U.S. Senate.
● Consciousness Raising groups began to be organized.
1968
● The Supreme Court struck down segregated job ads.
● The first national women's liberation conference was held.
1969
● California adopted the first no-fault divorce law in the nation.
1970
● More radical books were published (Sexual Politics, The Female Eunuch, Sisterhood is Powerful)
● Feminist Bella Abzug was elected to Congress, declaring “a woman's place is in the House.”
● The Lutheran Church begins ordaining women.
1971
● The Supreme Court ruled against sexual discrimination in hiring
1972
● Equal Rights Amendment prohibiting sex discrimination passed the Senate and was sent to states for ratification.
● Title IX of the Education Amendments of 1972 prohibited sex discrimination in high schools and colleges.
● Gloria Steinem launched the feminist magazine, Ms.
● The first battered woman's shelter opened in Urbana, Illinois
1973
● The Roe v. Wade decision declared that laws prohibiting abortion were unconstitutional but allowed state restrictions during the first trimester.
1974
● The Equal Credit Opportunity Act prohibited discrimination in consumer credit practices.
● Over 1,000 colleges began offering women's studies courses.
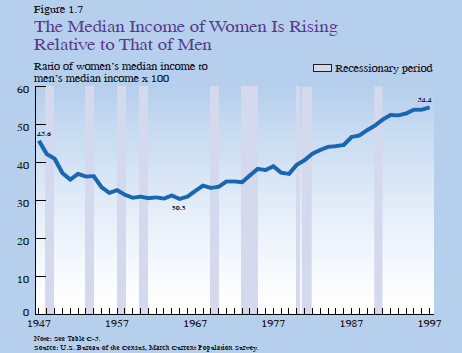
THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MALE AND FEMALE INCOME
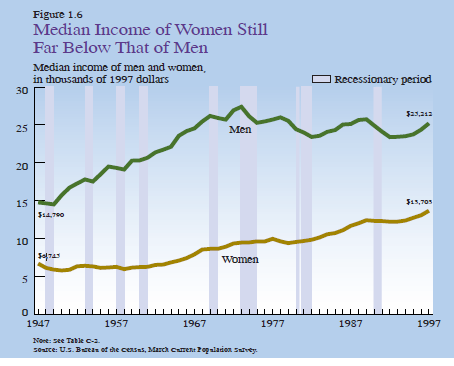
THE CHANGING RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN MALE AND FEMALE INCOME